Definitions of Counseling Psychology
Counseling psychology is a wide-ranging specialty within specialized psychology concerned with using psychological principles to enhance and promote the positive growth, well-being, and psychological wellbeing of persons, relations, collections, and the wider community.
Rendering to Carl Rogers “Counseling is a sequence of straight associates with the individual which purposes to proposal his support in moving his attitude & performances”
According to the New Zealand Psychologists Board (2013) Counseling Psychologist” – Counseling Psychologists put on psychological facts and philosophy resulting from research to the part of client authorization and improvement, to contribution children, beginning persons, grown-ups and their relations with personal, social, instructive, and occupational functioning by using psychological evaluations and interferences, and pre-emptive approaches that recognize environmental, developmental besides phenomenological magnitudes.
Significant highlights in the history of Counseling and psychotherapy
- Sigmund Freud: Psychoanalysis theory ; Id. Ego, Superego concept (1886)
- Carl Rogers: Client-Centered Therapy approach in his book (1951)
- Fritz Perls, Paul Goodman, and Ralph Hefferline: Gestalt therapy in the book Excitement and Growth in the Human Personality (1951)
- Abraham Maslow: Humanistic psychology (1954)
- Albert Ellis: Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy ( REBT) (1955)
- Viktor Frankl: Logotherapy; published “ Man’s Search for Meaning” English edition. This is an existential approach to counseling. Logotherapy (1959)
- Aaron Beck: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) (1967)
Key components of counseling
The basic stages of counseling are:
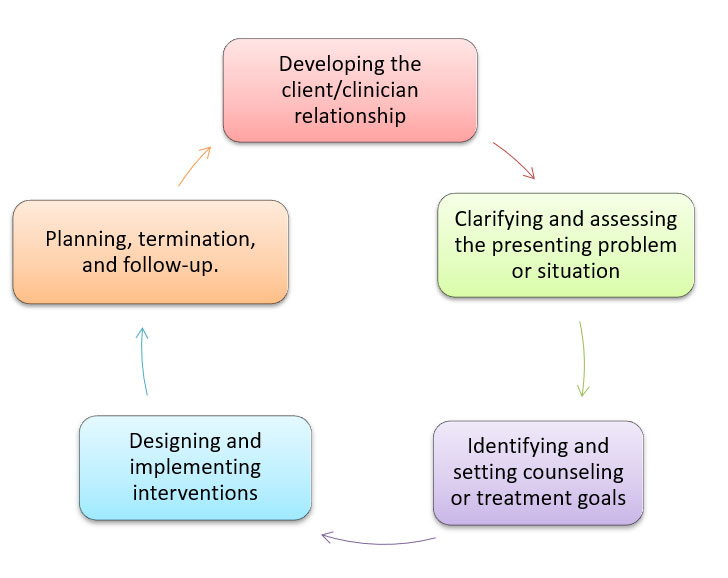
Nature and scope of counseling
Nature
- Individual/one to one helping relationship
- Face to face relationship
- Key focus: Person’s development, alteration, problematic explaining, and judgment creating needs.
- Professional work ( Counsellors required the highest level of training & professional skills)
- Confidential & private process/ personal meeting.
Scope (Individual counseling)
- Anxiety
- Anger management
- Depression
- Stress management
- Work place stress & relationships
- Relationships: personal and interpersonal dynamics
- Sexual abuse recovery
Goals of counseling
- Achievement of positive mental health (Self-actualization, realizing)
- Resolution of problems
- Improving personal effectiveness
- To aid the change process
- Improving decision- making
- Preventing the future occurrences of issues
- Behaviour modification
